Spring MVC (Model-View-Controller) is a powerful framework within the Spring ecosystem designed for developing web applications. It follows the MVC design pattern, which helps separate concerns, making applications modular, scalable, and easier to maintain. In this article, we’ll explore the architecture of Spring MVC, its components, and how it processes requests.
1. What is Spring MVC?
Spring MVC is a part of the Spring Framework that provides an elegant way to develop web applications using the Model-View-Controller (MVC) architecture. It simplifies the development of web applications by leveraging dependency injection (DI) and integrating seamlessly with other Spring components such as Spring Boot, Spring Security, and Spring Data.
2. Spring MVC Architecture Overview
Spring MVC follows the MVC pattern, which divides the application into three primary components:
- Model – Represents the data and business logic.
- View – Handles the presentation layer (HTML, JSP, Thymeleaf, etc.).
- Controller – Manages request handling and interacts with the model and view.
Spring MVC also follows the Front Controller design pattern, where a single dispatcher (DispatcherServlet) handles all incoming requests.
Spring MVC Request Flow
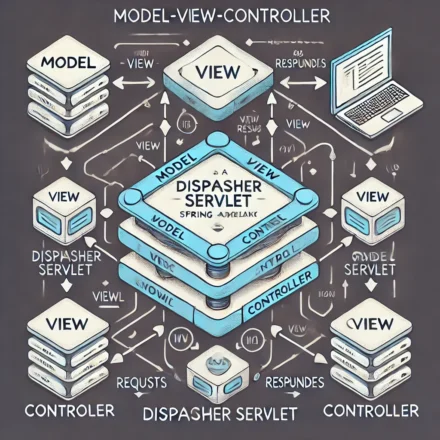
When a client sends a request to a Spring MVC application, the following process occurs:
- Client Request: The client sends an HTTP request.
- DispatcherServlet: The request is received by
DispatcherServlet, which acts as the Front Controller. - Handler Mapping: It finds the appropriate controller method based on the request URL.
- Controller Processing: The controller method is executed and processes the request.
- Service Layer Interaction (optional): If business logic is required, the controller interacts with the service layer (which may communicate with a database via the DAO layer).
- Model & View Resolution: The controller returns a
ModelAndViewobject that contains the model (data) and the view name. - View Resolver: The
ViewResolverfinds the appropriate view (JSP, Thymeleaf, etc.) based on the view name. - Response to Client: The resolved view is rendered, and the response is sent back to the client.
3. Key Components of Spring MVC
1. DispatcherServlet (Front Controller)
- Acts as the entry point for all requests.
- Delegates requests to appropriate controllers.
- Configured in
web.xml(for XML-based configuration) or via Java-based configuration (@Configuration).
2. Handler Mapping
- Maps incoming requests to appropriate controllers.
- Example:
@RequestMapping("/home")in a controller maps requests to/home.
3. Controller
- Handles requests and processes data.
- Annotated with
@Controlleror@RestController. - Example:
javaCopyEdit@Controller
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping
public String sayHello(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("message", "Hello, Spring MVC!");
return "helloView"; // View name
}
}
4. Model and ModelMap
- Stores data to be passed to the view.
- Example:
javaCopyEditmodel.addAttribute("key", value);
5. View Resolver
- Resolves logical view names into actual view files.
- Example: If
helloViewis returned, the view resolver maps it to/WEB-INF/views/hello.jsp.
6. View (JSP, Thymeleaf, etc.)
- The UI part of the application.
- Example of a JSP view:
jspCopyEdit<h1>${message}</h1>
4. Spring MVC Example Project
Step 1: Add Dependencies (Spring Boot Example)
If you’re using Spring Boot, include these dependencies in pom.xml:
xmlCopyEdit<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
Step 2: Create a Spring Boot Application
javaCopyEdit@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringMvcDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringMvcDemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
Step 3: Create a Controller
javaCopyEdit@RestController
@RequestMapping("/greet")
public class GreetingController {
@GetMapping
public String greet() {
return "Hello, Welcome to Spring MVC!";
}
}
Step 4: Run and Test
- Run the application and visit
http://localhost:8080/greetin the browser.
5. Advantages of Spring MVC
✅ Separation of Concerns – Divides logic into Model, View, and Controller.
✅ Flexible View Resolvers – Supports JSP, Thymeleaf, PDF, and more.
✅ Built-in Security – Easily integrates with Spring Security.
✅ Extensibility – Integrates with REST, WebSockets, and microservices.
✅ Robust Exception Handling – Supports @ExceptionHandler.
6. Conclusion
Spring MVC provides a well-structured way to build scalable Java-based web applications. It efficiently separates concerns, making development more organized and maintainable. Whether you’re developing traditional web apps or RESTful APIs, Spring MVC is a go-to framework in enterprise development.

